%GEOM Card
This card is used to describe the problem geometry in the rectangular coordinate system. This card is mandatory. The coordinate system used in ADPRES is shown in the following figure
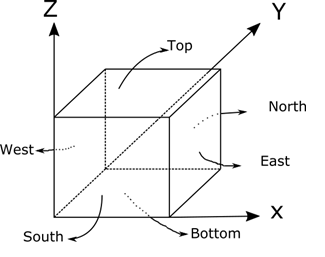
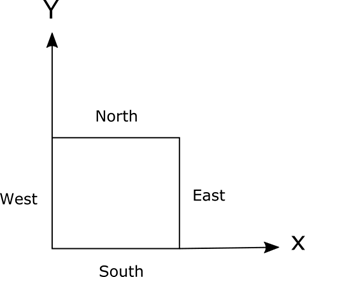
The point of origin is located at the corner between west, bottom and south sides. The next figure shows the coordinate system for radial planar map (seen from top) which typically used for two-dimensional problems.
Following is the description of the %GEOM card
%GEOM |
Variable | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINE 1 | NX | Number of assemblies along X-direction | NX at least equal to 2 |
| NY | Number of assemblies along Y-direction | NY at least equal to 2 | |
| NZ | Number of assemblies along Z-direction | NZ at least equal to 2 | |
| LINE 2 | XSIZE(1:NX) | Assembly size along X-direction(from west to east) | |
| LINE 3 | XDIV(1:NX) | Assembly division along X-direction(from west to east) | |
| LINE 4 | YSIZE(1:NY) | Assembly size along Y-direction(from south to north) | |
| LINE 5 | YDIV(1:NY) | Assembly division along Y-direction(from south to north) | |
| LINE 6 | ZSIZE(1:NZ) | Assembly size along Z-direction(from bottom to top) | |
| LINE 7 | ZDIV(1:NZ) | Assembly division along Z-direction(from bottom to top) | |
| LINE 8 | NP | Number of different core planar with different material composition | |
| LINE 9 | ZPLN(1:NZ) | Planar assignment along axial or z-direction from bottom to top (see the example below) | |
| LINE 10 | ASM(1:NX) | Radial planar material map | Repeat this line NY times to form a core planar material map. Then, repeat this planar map NP times |
| LINE 11 | XEAST | East boundary conditions | 0 = Zero flux |
| XWEST | West boundary conditions | 1 = Zero incoming current | |
| YNORTH | North boundary conditions | 2 = Reflective | |
| YSOUTH | South boundary conditions | ||
| ZBOTT | Bottom boundary conditions | ||
| ZTOP | Top boundary conditions |
Below you can find various %GEOM card examples for one, two and three-dimensional problems.
Example of a %GEOM card for 3D problem
Three-dimensional problem with 2x2 nodes per FA
! Typical %GEOM CARD for 3D problem with 2x2 nodes per FA
%GEOM
9 9 19 !nx, ny, nz
10.0 8*20.0 !x-direction assembly size in cm
1 8*2 !x-direction assembly divided into 2 (10 cm each)
8*20.0 10.0 !y-direction assembly size in cm
8*2 1 !y-direction assembly divided into 2 (10 cm each)
19*20.0 !z-direction assembly in cm
19*1 !z-direction nodal is not divided
4 !np number of planar type
1 13*2 4*3 4 !planar assignment (from bottom to top)
! Planar_type_1 (Bottom Reflector)
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 0
4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0
! Planar_type_2 (Fuel)
3 2 2 2 3 2 2 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 4
3 2 2 2 3 1 1 4 0
2 2 2 2 1 1 4 4 0
2 2 1 1 1 4 4 0 0
1 1 1 4 4 4 0 0 0
4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0
! Planar_type_3 (Fuel+Partial Control Rods)
3 2 2 2 3 2 2 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4
2 2 3 2 2 2 1 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 4
3 2 2 2 3 1 1 4 0
2 2 2 2 1 1 4 4 0
2 2 1 1 1 4 4 0 0
1 1 1 4 4 4 0 0 0
4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0
! Planar_type_4 (Top reflectors)
5 4 4 4 5 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 5 4 4 4 4 4 4
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
5 4 4 4 5 4 4 4 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 0 0
4 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 0
4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0
! Boundary conditions
! 0 = zero-flux
! 1 = zero-incoming current
! 2 = reflective
!(east), (west), (north), (south), (bottom), (top)
1 2 2 1 1 1
Example of %GEOM card for 2D problems
Two-dimensional problem with 2x2 nodes per FA
! Typical %GEOM CARD for 2D problem with 2x2 nodes per FA
%GEOM
9 9 2 !nx, ny, nz
11.5613 8*23.1226 !x-direction assembly size in cm
1 8*2 !x-direction assembly divided into 2 (10 cm each)
8*23.1226 11.5613 !y-direction assembly size in cm
8*2 1 !y-direction assembly divided into 2 (10 cm each)
2*11.5613 !z-direction assembly in cm
2*1 !z-direction nodal is not divided
1 !np number of planar type
2*1 !planar assignment (from bottom to top)
! Planar_type_1 (Bottom Reflector)
1 8 2 6 1 7 1 4 3
8 1 8 2 8 1 1 4 3
2 8 1 8 2 7 1 4 3
6 2 8 2 8 1 8 4 3
1 8 2 8 2 5 4 3 3
7 1 7 1 5 4 4 3 0
1 1 1 8 4 4 3 3 0
4 4 4 4 3 3 3 0 0
3 3 3 3 3 0 0 0 0
! Boundary conditions
! 0 = zero-flux
! 1 = zero-incoming current
! 2 = reflective
!(east), (west), (north), (south), (bottom), (top)
1 2 2 1 2 2
Two-dimensional problem with 16x16 nodes per FA. Normally for Finite Difference Method (FDM) calculations
! Typical %GEOM CARD for 2D problem with 16x16 nodes per FA
%GEOM
9 9 2 !nx, ny, nz
10.0 8*20.0 !x-direction assembly size in cm
8 8*16 ! 16x16 per FA
8*20.0 10.0 !y-direction assembly size in cm
8*16 8 ! 16x16 per FA
2*1.25 !z-direction assembly in cm
2*1 !z-direction nodal is not divided
1 !np number of planar type
2*1 !planar assignment (from bottom to top)
! Planar_type_1 (Bottom Reflector)
3 2 2 2 3 2 2 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 4
3 2 2 2 3 1 1 4 0
2 2 2 2 1 1 4 4 0
2 2 1 1 1 4 4 0 0
1 1 1 4 4 4 0 0 0
4 4 4 4 0 0 0 0 0
! Boundary conditions
! 0 = zero-flux
! 1 = zero-incoming current
! 2 = reflective
!(east), (west), (north), (south), (bottom), (top)
1 2 2 1 2 2
Example of good %GEOM card for 1D problems
One-dimensional problem with 1 cm node or mesh size
! Typical %GEOM CARD for 1D problem with 1 cm node or mesh size
%GEOM
5 2 2 !nx, ny, nz
5*20.0 !x-direction assembly size in cm
5*20 !x-direction assembly divided into 20 (1 cm each)
2*1.0 !y-direction assembly size in cm
2*1 !y-direction nodal is not divided
2*1.0 !z-direction assembly in cm
2*1 !z-direction nodal is not divided
1 !np number of planar type
2*1 !planar assignment (from bottom to top)
! Planar_type_1 (Bottom Reflector)
5 4 3 2 1
5 4 3 2 1
! Boundary conditions
! 0 = zero-flux
! 1 = zero-incoming current
! 2 = reflective
!(east), (west), (north), (south), (bottom), (top)
2 1 2 2 2 2
IMPORTANT
It is recommended to make the node sizes (assemblies sizes and how you divide them) are as uniform as possible to improve the stability of the calculations. An example of a BAD %GEOM card is
! A BAD EXAMPLE OF %GEOM CARD
%GEOM
19 19 27 !nx, ny, nz
19*20.0 !x-direction assembly size is 20 cm
19*2 !x-direction assembly division (node size 10 cm) -> GOOD
19*20.0 !y-direction assembly size is 20 cm
19*2 !y-direction assembly division (node size 10 cm) -> GOOD
70.0 15.240 20*17.526 15.240 4*20.0 !z-direction assembly size in cm
1 1 20*1 1 4*1 !z-direction assembly division -> BAD
4 !np number of planar type
1 2 20*3 2 4*4
..
..
..
(TILL END)
In the example above, the node size for bottom reflector is 70 cm, while the node size in z-direction as well as other x- and y-directions are between 10 cm - 20 cm. This %GEOM card can lead to instability of the calculations. That %GEOM card can be changed as follow to make the calculation stable
! A GOOD EXAMPLE OF %GEOM CARD
%GEOM
19 19 27 !nx, ny, nz
19*20.0 !x-direction assembly size is 20 cm
19*2 !x-direction assembly division (node size 10 cm) -> GOOD
19*20.0 !y-direction assembly size is 20 cm
19*2 !y-direction assembly division (node size 10 cm) -> GOOD
70.0 15.240 20*17.526 15.240 4*20.0 !z-direction assembly size in cm
7 2 20*2 2 4*2 !z-direction assembly division -> GOOD
4 !np number of planar type
1 2 20*3 2 4*4
..
..
..
(TILL END)
We just made the node sizes more uniform now. First, we divided the 70 cm bottom reflector into 7 nodes (means 10 cm node size). We also divided other z-direction assembly size two each to make them more uniform.